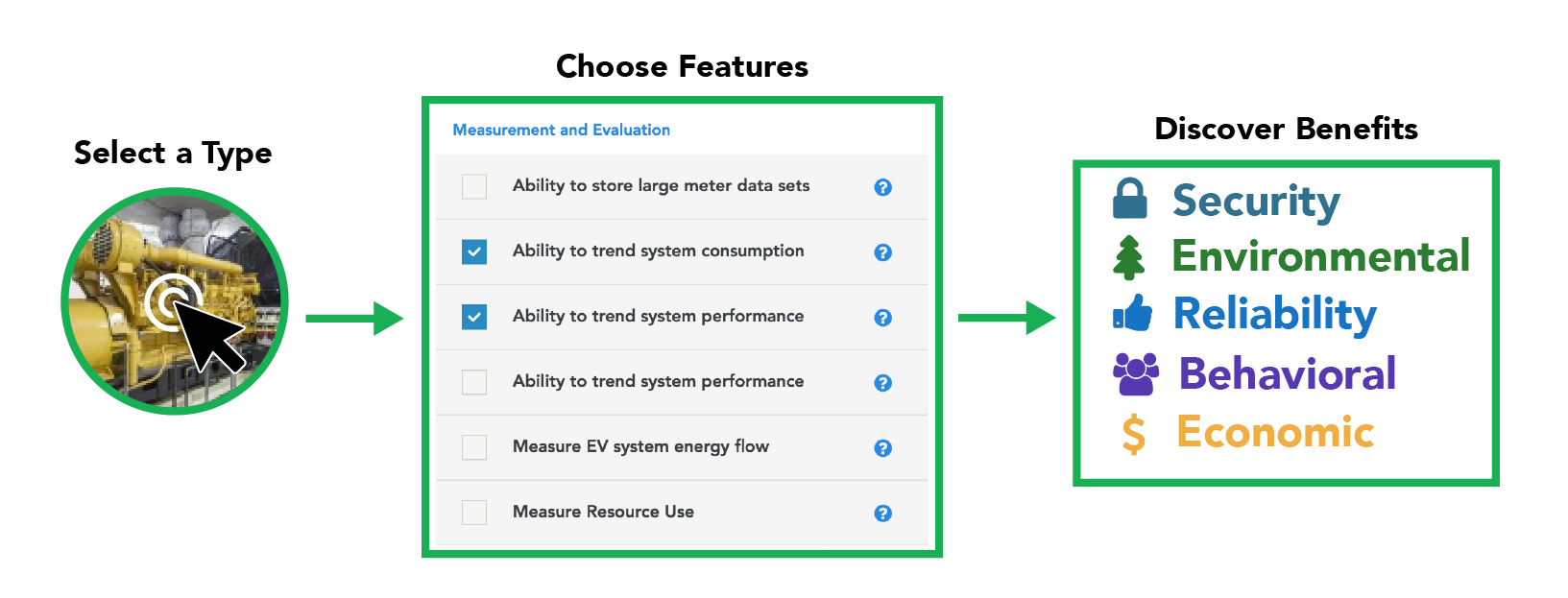
Submetering Wizard Select a meter type

Electrical Circuit

Electrical System

Electrical - End Use Device

Gas

Water
What do you want to accomplish with Submetering?
The Submetering Wizard provides information about the comprehensive uses and benefits of submetering systems. Use the wizard to learn about submetering features and benefits by submeter type. You can also mark which benefits you’ve already attained in an already installed system and print or export a customized list of benefits.
Wizard Process
Electrical Circuit
Electrical circuit submeters measure resource use of a single panel, or submeters can be placed at multiple points within a panel system, or at branches of a circuit to measure resource use of multiple circuits. Circuit submeters enable occupant energy-use behavioral awareness, improved tenant billing, enhanced space resource use, and optimized operations and maintenance programs.
Select submeter features below and click continue to learn more about the range of associated direct and indirect benefits.
Electrical System
System-level electric submeters enable management to easily control systems such as lighting, heating and cooling, and control start and stop times from one central platform. System-level submetering enhances the O&M Staff's ability to analyze specific energy load performance at the system-level, benchmark and optimize building performance, and enables more refined project measurement and verification.
Select submeter features below and click continue to learn more about the range of associated direct and indirect benefits.
Electrical - End Use Device
End-use submetering provides the finest data resolution for energy and resource use of a particular system or equipment type for more detailed analysis. An objective of end-use submetering is to monitor equipment performance of high energy users in order to identify technology inefficiencies and validate savings estimates. Chillers, boilers, cooling towers, pumps, and motors are examples of equipment that are submetered to capture more granular performance metrics. End-use submeters can provide informative feedback mechanisms and data that can influence occupant behavior and tenant practices, such as turning off computers and other ancillary devices.
Select submeter features below and click continue to learn more about the range of associated direct and indirect benefits.
Gas
Natural gas submeters measure the flow rate of natural gas and usage for billing. Monitoring natural gas flow rates and consumption at individual zones helps in assessing process efficiencies, identifying unusual consumption points, promoting conservation, and providing a means for cost allocation to various operating areas. Typically, the largest consumption of natural gas is used for heating.
Select submeter features below and click continue to learn more about the range of associated direct and indirect benefits.
Water
Water submeters are used to measure the quantity of water used by a facility, building, building area, device for indoor or outdoor water use, and potable or non-potable water users. Water submeters help to detect water losses, identify water conservation and efficiency measures, and provides helpful information for the rate of water usage and conservation incentives.
Select submeter features below and click continue to learn more about the range of associated direct and indirect benefits.