Ventilation Fan Belts, Synchronous and Cogged
Last Updated: 02/27/24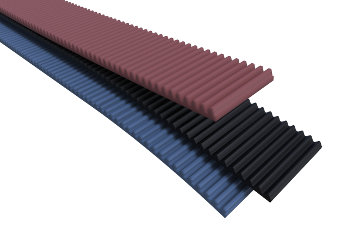
A ventilation fan belt is a belt, driven by the crankshaft of an engine, that turns a fan for drawing cooling air through the radiator. Synchronous drive belts are designed to reduce both belt slippage and frictional losses. Cogged V-belts are designed to reduce the bending resistance as the belt travels around the sheave (pulley) and have less frictional losses than standard V-belts.
 Product Details
Product Details
|
Procurement Info
|
Where to Buy
|
|---|---|
 Life Cycle Cost Savings
Life Cycle Cost Savings
Life Cycle Costing (LCC) aims to quantify the financial impact of a product over its entire life cycle to assist consumers in making decisions that will save them money over the long term.
GSA's Proving Ground![]() found that the use of cogged V-belts and synchronous-drive fan belts are a low-investment way to reduce the inefficiencies in ventilation fans caused by bel slippage and bending resistance. GPG found an energy savings of 2 - 20% for synchronous belts, with about half that savings for cogged fan belts. Payback is between 1 and 4 years, depending on the type of fan belt.
found that the use of cogged V-belts and synchronous-drive fan belts are a low-investment way to reduce the inefficiencies in ventilation fans caused by bel slippage and bending resistance. GPG found an energy savings of 2 - 20% for synchronous belts, with about half that savings for cogged fan belts. Payback is between 1 and 4 years, depending on the type of fan belt.
 Guiding Principles
Guiding Principles
Contributes to meeting The Guiding Principles for Sustainable Federal Buildings
 Additional Guidance
Additional Guidance
GSA's Green Proving Ground recommends replacing V-belts with synchronous drive belts on all variable air volume (VAV) fans. On constant volume (CV) fans, belts should be replaced at end-of-life with cogged V-belts.

 GSA's Green Proving Ground
GSA's Green Proving Ground